The Center for Automotive Research’s (CAR) Coalition for Automotive Lightweighting Materials (CALM) released a Roof Lightweighting Study aimed at highlighting the possibilities of mixed-material for mass reduction.
A 2011 Honda Accord with a 270 MPa mild steel roof was selected as the baseline for the study, because of its potential for multi-material solutions. The roof is comprised of 12 parts including the roof panel, roof bows, roof rails, and the headers. The assembly weighed 22.5 kg (49.4 lbs) and was joined using spot welds and adhesive bonding.
CALM members (represented 30 materials companies and auto manufacturers) submitted lightweighting ideas for optimizing the 2011 roof assembly, which were were tested on various qualitative and quantitative parameters such as manufacturing readiness, joining feasibility, repairability, ability of computer simulation, etc. After filtering through various combinations of these ideas, the project team ultimately selected three of these concepts to be used in the study. All three concepts were compared to the baseline in terms of reduced weight and comparable performance and were studied using computer aided engineering methods, including finite element analysis and design of experiments. In all cases, secondary mass reduction could be achieved by optimizing other parts and systems, such as wheels, powertrain, suspension, bumpers, electrical systems and wiring, etc.
Concept 1 was a 100% steel solution, which utilized press-hardened or third-generation steels (1,500 MPa and 980 MPa, respectively) for most structures. Spot-welds and adhesive bonding were used between roof and roof bows. The concept provided a mass reduction of 5 kg (11 lbs), around 22%.
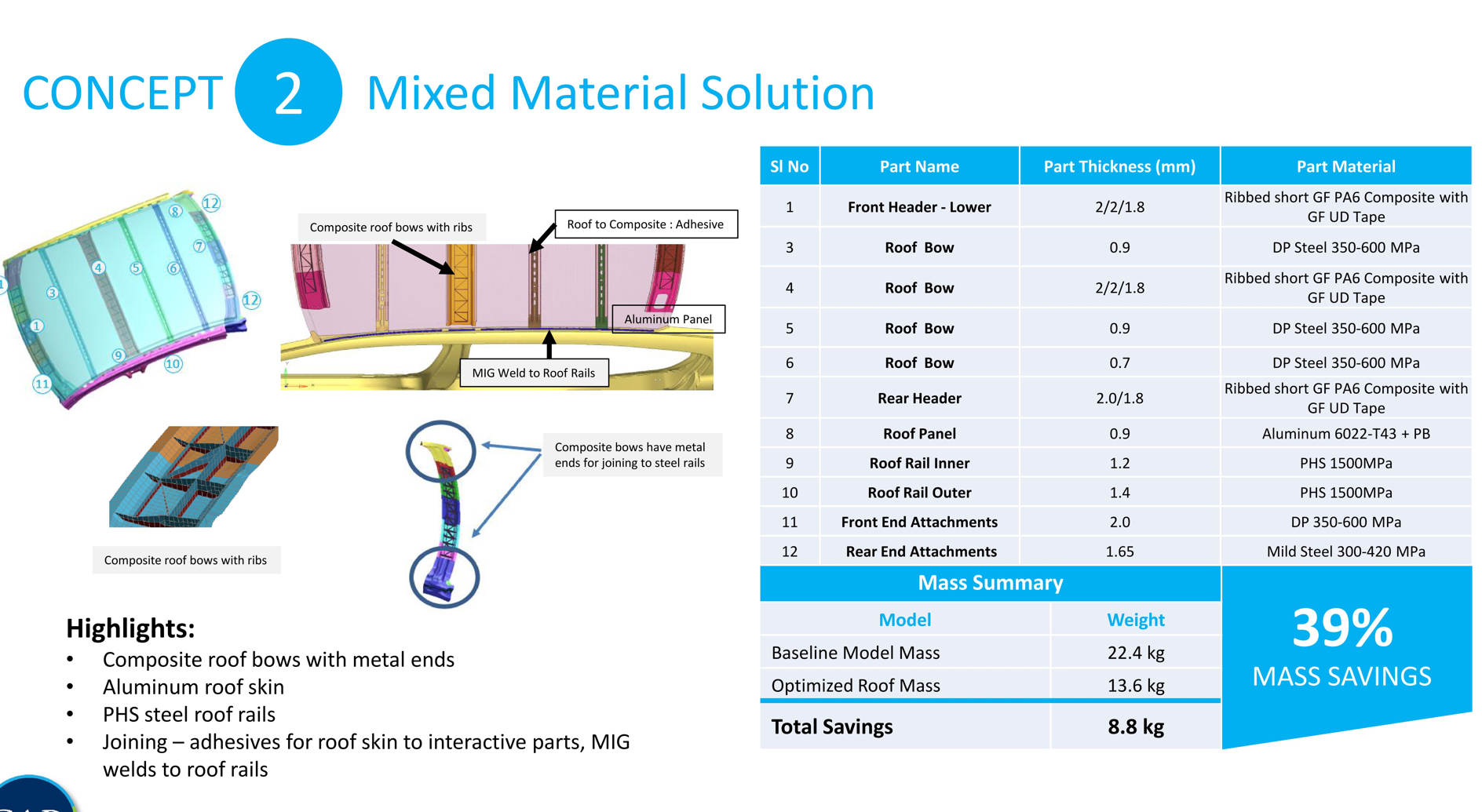
Concept 2 implemented a mixed-material strategy, in which aluminum was used for the roof panel, steel for the rails, and glass-fiber composites for the roof bows. The structure was joined using adhesives for roof skin to interactive parts and MIG welds to roof rails. In addition to achieving a mass reduction of 39% (8.8 kg, or 19.4 lbs), the aluminum mixed-material design met or improved on the baseline Accord performance in all aspects except torsional stiffness, coming in at 78% of the original Accord’s specifications. “If our design space was bigger, we could meet target torsion stiffness by taking a small hit on the percentage of mass reduction achieved,” noted the CALM study.
Concept 3 implemented a similar mixed-material design and joining to concept 2, with carbon fiber in place of aluminum for the roof panel. The design reduced the mass by 9 kg (19.8 lbs), or 40%. Although a slightly higher mass reduction compared to the aluminum solution, the carbon fiber concept showed increased cost. In addition, the carbon fiber solution did not achieved the same level of performance, meeting only 74% of the study’s goal.
The complete study can be found online.