Apple unveiled a plan to become carbon neutral across its entire business, manufacturing supply chain, and product life cycle by 2030. According to the company, it is already carbon neutral today for its global corporate operations. This new commitment will mean that by 2030, every Apple device sold will have net zero climate impact.
“Businesses have a profound opportunity to help build a more sustainable future, one born of our common concern for the planet we share,” said Tim Cook, Apple’s CEO. “The innovations powering our environmental journey are not only good for the planet — they’ve helped us make our products more energy efficient and bring new sources of clean energy online around the world. Climate action can be the foundation for a new era of innovative potential, job creation, and durable economic growth. With our commitment to carbon neutrality, we hope to be a ripple in the pond that creates a much larger change.”
In its 2020 Environmental Progress Report, Apple details its plans to reduce emissions by 75% by 2030, while developing innovative carbon removal solutions for the remaining 25% of its comprehensive footprint. The company’s roadmap involves a number of factors, including low carbon product design, expanding energy efficiency, renewable energy, process and material innovations, and carbon removal.
Aluminum is expected to play an important role in Apple’s plan to achieve carbon neutrality.
Recycling
Apple plans to continue to increase the use of low carbon and recycled materials in its products, innovate in product recycling, and design products to be as energy efficient as possible.
All of the company’s iPhone, iPad, Mac, and Apple Watch devices released in the past year are made with recycled content. In particular, the MacBook Air and Mac mini computers are made with 100% recycled aluminum, and the iPhone Taptic Engine is comprised with 100% recycled rare earth elements — a first for Apple and for any smartphone.
The company has also invested in innovations designed to improve recycling throughout its operations, such as new robots that disassemble electronics to recover valuable materials. Apple launched a new recycling robot, called Daisy, across a number of its material recovery locations in 2019. The Daisy robot is designed to recover valuable materials, such as aluminum, from the iPhone. Meanwhile, the new robot, named Dave, disassembles the Taptic Engine from iPhone to better recover key materials, such as rare earth magnets and tungsten.
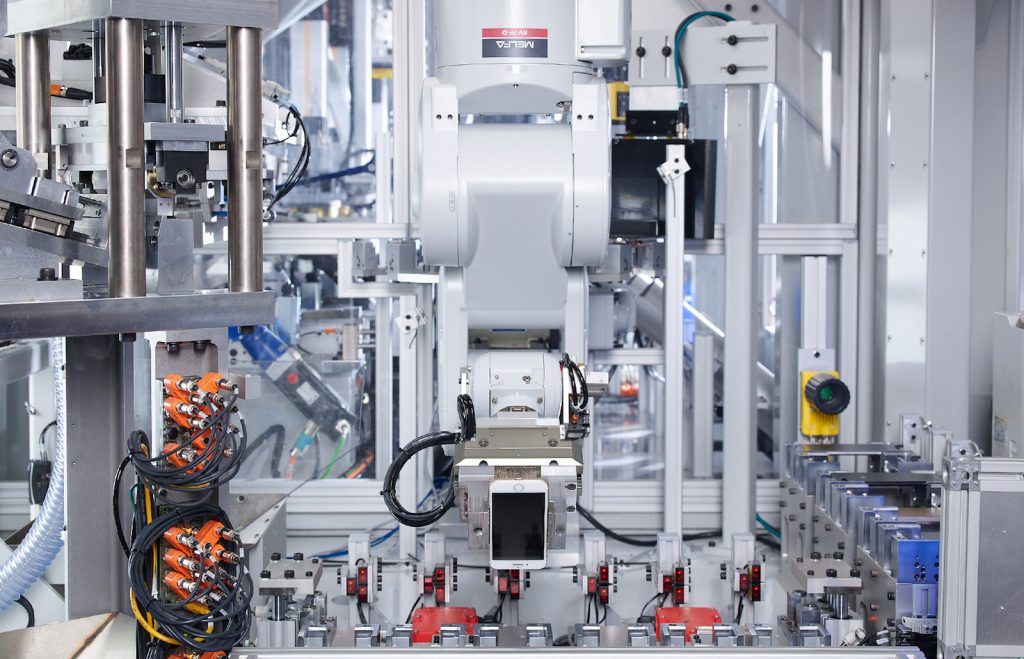
Through the design and use of recycled content innovations in its products, Apple decreased its carbon footprint by 4.3 million metric tons in 2019. Over the past 11 years, Apple has reduced the average energy needed for product use by 73%.
The company’s Material Recovery Lab in Austin, Texas, which is focused on innovative electronics recycling technology, is now partnering with Carnegie Mellon University to further develop engineering solutions.
Smelting
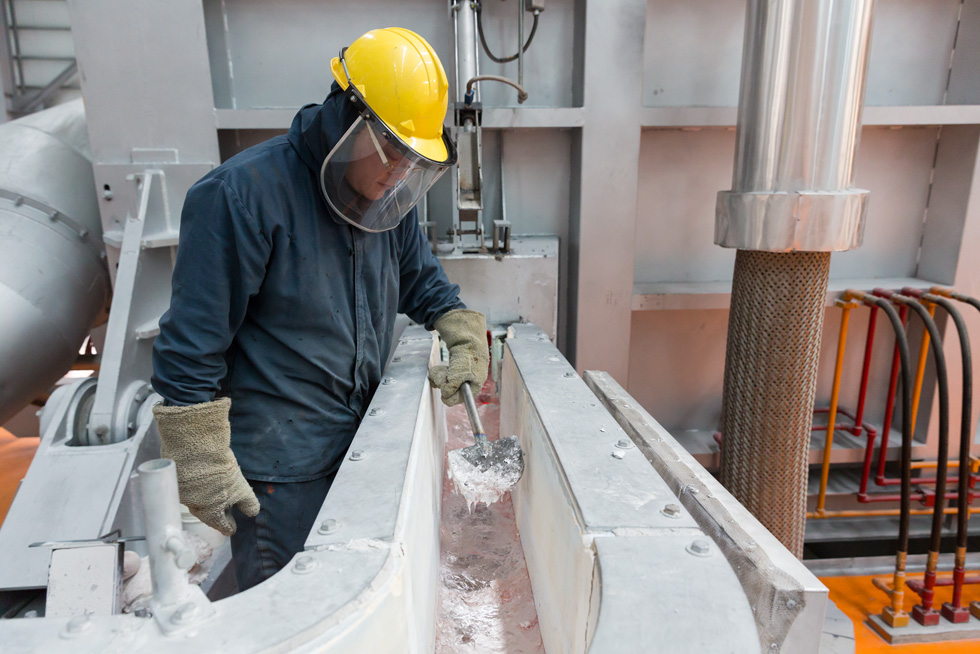
Apple is supporting the development of a primary aluminum process technology, expected to eliminate direct carbon dioxide emissions. This inert anode technology is being developed by Elysis, a joint venture between Alcoa and Rio Tinto. Investments from Apple are helping to accelerate the development process.
Elysis successfully produced its first commercial batch of aluminum in December 2019, which was purchased by Apple. This low-carbon aluminum is now being used in the production of the 16-inch MacBook Pro.